 | Part 3: API Quick Reference |  |

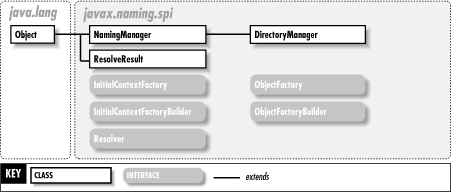
The javax.naming.spi package defines the service provider interface (SPI) for JNDI. Only system programmers who are developing JNDI providers need to use this package; JNDI application programmers can ignore it. The classes and interfaces in this package allow JNDI service providers to be plugged in underneath the JNDI API. Figure 24-1 shows the hierarchy of this package.
| DirectoryManager | JNDI 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| javax.naming.spi | ||
DirectoryManager is a subclass of NamingManager that contains a method for creating javax.naming.directory.DirContext objects.
| public class DirectoryManager extends NamingManager { | ||
| // | No Constructor | |
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static javax.naming.directory.DirContext getContinuationDirContext (CannotProceedException cpe) throws NamingException; | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->NamingManager-->DirectoryManager
| InitialContextFactory | JNDI 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| javax.naming.spi | ||
This interface represents a factory that creates an initial context for a naming or directory service. The initial context serves as the entry point into the service. A JNDI service provider always includes an InitialContextFactory that can be used as the value of the java.naming.factory.initial property
| public abstract interface InitialContextFactory { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract javax.naming.Context getInitialContext (java.util.Hashtable environment) throws NamingException; | ||
| } | ||
Returned By: InitialContextFactoryBuilder.createInitialContextFactory()
| InitialContextFactoryBuilder | JNDI 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| javax.naming.spi | ||
This interface represents a builder that creates initial context factories. A program can override the default initial context factory builder by calling NamingManager.setInitialContextFactoryBuilder() and specifying a new builder. Such a builder must implement this interface.
| public abstract interface InitialContextFactoryBuilder { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract InitialContextFactory createInitialContextFactory (java.util.Hashtable environment) throws NamingException; | ||
| } | ||
Passed To: NamingManager.setInitialContextFactoryBuilder()
| NamingManager | JNDI 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| javax.naming.spi | ||
The NamingManager class contains methods for creating javax.naming.Context objects and otherwise controlling the operation of the underlying service provider.
| public class NamingManager { | ||
| // | No Constructor | |
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static javax.naming.Context getContinuationContext (CannotProceedException cpe) throws NamingException; | ||
| public static javax.naming.Context getInitialContext (java.util.Hashtable environment) throws NamingException; | ||
| public static Object getObjectInstance (Object refInfo, Name name, javax.naming.Context nameCtx, java.util.Hashtable environment) throws Exception; | ||
| public static javax.naming.Context getURLContext (String scheme, java.util.Hashtable environment) throws NamingException; | ||
| public static boolean hasInitialContextFactoryBuilder (); | synchronized | |
| public static void setInitialContextFactoryBuilder (InitialContextFactoryBuilder builder) throws NamingException; | synchronized | |
| public static void setObjectFactoryBuilder (ObjectFactoryBuilder builder) throws NamingException; | synchronized | |
| } | ||
Subclasses: DirectoryManager
| ObjectFactory | JNDI 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| javax.naming.spi | ||
This interface represents a factory for creating objects. JNDI supports the dynamic loading of object implementations with object factories. For example, say you have a naming system that binds file objects to names in the namespace. If the filesystem service provider binds filenames to Reference objects, a Reference object can create a file object through an object factory. This means that a call to lookup() a filename (in the appropriate Context) returns an actual file object the programmer can manipulate as necessary. An ObjectFactory is responsible for creating objects of a specific type.
| public abstract interface ObjectFactory { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract Object getObjectInstance (Object obj, Name name, javax.naming.Context nameCtx, java.util.Hashtable environment) throws Exception; | ||
| } | ||
Returned By: ObjectFactoryBuilder.createObjectFactory()
| ObjectFactoryBuilder | JNDI 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| javax.naming.spi | ||
This interface represents a builder that creates object factories. A program can override the default object factory builder by calling NamingManager.setObjectFactoryBuilder() and specifying a new builder. Such a builder must implement this interface.
| public abstract interface ObjectFactoryBuilder { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract ObjectFactory createObjectFactory (Object obj, java.util.Hashtable info) throws NamingException; | ||
| } | ||
Passed To: NamingManager.setObjectFactoryBuilder()
| Resolver | JNDI 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| javax.naming.spi | ||
The Resolver interface contains methods that are implemented by objects that can act as intermediate contexts for naming resolution purposes.
| public abstract interface Resolver { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract ResolveResult resolveToClass (Name name, Class contextType) throws NamingException; | ||
| public abstract ResolveResult resolveToClass (String name, Class contextType) throws NamingException; | ||
| } | ||
| ResolveResult | JNDI 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| javax.naming.spi | ||
This class represents the result of resolving a name.
| public class ResolveResult { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public ResolveResult (Object robj, Name rname); | ||
| public ResolveResult (Object robj, String rcomp); | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected ResolveResult (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void appendRemainingComponent (String name); | ||
| public void appendRemainingName (Name name); | ||
| public Name getRemainingName (); | ||
| public Object getResolvedObj (); | ||
| public void setRemainingName (Name name); | ||
| public void setResolvedObj (Object obj); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Fields | |
| protected Name remainingName ; | ||
| protected Object resolvedObj ; | ||
| } | ||
Returned By: Resolver.resolveToClass()

Copyright © 2001 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.